NFT and DWC System

Introduction
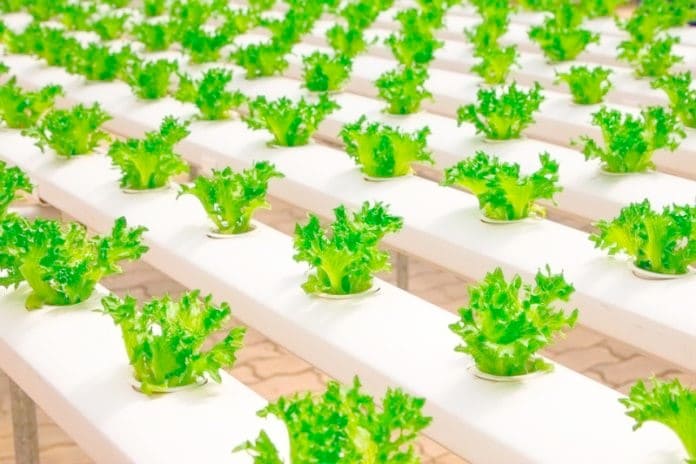
Hydroponics is the art of gardening without soil. Hydroponics is a Latin word meaning “working water.” In the absence of soil, water goes to work providing nutrients, hydration, and oxygen to plant life. From watermelons to jalapeños to orchids, plants flourish under the careful regimen of hydroponics. Using minimal space, 90% less water than traditional agriculture, and ingenious design, hydroponic gardens grow beautiful fruits and flowers in half the time. Though the technology sounds cutting-edge, the history of hydroponics dates back to the famed Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The Euphrates River was diverted into channels that cascaded down the lavish garden walls. In the 13th century, Marco Polo wrote of witnessing floating gardens in China. However, hydroponics is far from merely an innovation of the ancient ages. In the 1990s, NASA grew aeroponic bean seedlings in zero gravity aboard a space station, opening up the possibility of sustainable agriculture in space. Hydroponics continues to be a timeless and dynamic method of water conservation and crop production. Hydroponic crop production has significantly increased in recent years worldwide, as it allows a more efficient use of water and fertilizers, as well as a better control of climate and pest factors. Furthermore, hydroponic production increases crop quality and productivity, which results in higher competitiveness and economic incomes. Among factors affecting hydroponic production systems, the nutrient solution is consider yield and quality. Hydroponics is a way to skip the soil, sub in a different material to support the roots of the plant, and grow crops directly in nutrient-rich water. There are multiple approaches to designing hydroponic systems, but the core elements are essentially the same.
What you need: ?
Fresh water- Water quality is an important determinative factor in hydroponics cultivation. Water is the basic ‘carrier’ in hydroponics as it dissolves and transports nutrients for plants.
Oxygen – Oxygen is critical in the development and growth of edible crops grown in hydroponic systems such as nutrient film technique (NFT) and deep water raft culture.A method that organic growers use to increase oxygen levels is cascading the water when it returns to the reservoir. As water returns it is allowed to fall and break the surface of the reservoir so that the water can pull in oxygen.
Root Support.- Hydroponic growing eliminates many of the problems often associated with gardening, since there aren’t any burrowing animals or soil-borne pests to worry about. Root crops such as turnips, radishes, carrots, leafy vegetable and herbs can all be grown hydroponically. While they will grow fine using various types of hydroponic methods, one of the easiest ways is an Dwc, Nft flow and ebb system that uses enough growing media to support the plants from start to finish.
Nutrients – These are nutrients that plants need to absorb in large quantities. They are the most vital nutrient minerals you must take care of first. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium. These three nutrients are absorbed in the largest quantities by plants and are known as macro nutrients. They serve absolutely vital roles in a plant’s development.
How does Hydroponics work?
Hydroponic systems work by allowing minute control over environmental conditions like temperature and pH balance and maximised exposure to nutrients and water. Hydroponics operates under a very simple principle: provide plants exactly what they need when they need it. Hydroponics administer nutrient solutions tailored to the needs of the particular plant being grown. They allow you to control exactly how much light the plants receive and for how long. pH levels can be monitored and adjusted. In a highly customised and controlled environment, plant growth accelerates.
By controlling the environment of the plant, many risk factors are reduced. Plants grown in gardens and fields are introduced to a host of variables that negatively impact their health and growth. Fungus in the soil can spread diseases to plants. Wildlife like rabbits can plunder ripening vegetables from your garden. Pests like locusts can descend on crops and obliterate them in an afternoon. Hydroponic systems end the unpredictability of growing plants outdoors and in the earth. Without the mechanical resistance of the soil, seedlings can mature much faster. By eliminating pesticides, hydroponics produce much healthier and high-quality fruits and vegetables. Without obstacles, plants are free to grow vigorously and rapidly.
What are the components of a hydroponic system?
To maintain a flourishing hydroponic system, you will need to become acquainted with a few components that make hydroponics run efficiently.
Growing media
Hydroponic plants are often grown in inert media that support the plant’s weight and anchor its root structure. Growing media is the substitute for soil, however, it does not provide any independent nutrition to the plant. Instead, this porous media retains moisture and nutrients from the nutrient solution which it then delivers to the plant. Many growing media are also pH-neutral, so they will not upset the balance of your nutrient solution. There are a host of different media to choose from, and the specific plant and hydroponic system will dictate which media best suits your endeavor. Hydroponic growing media is widely available both online and at local nurseries and gardening stores.
Air stones and air pumps
Plants that are submerged in water can quickly drown if the water is not sufficiently aerated. Air stones disperse tiny bubbles of dissolved oxygen throughout your nutrient solution reservoir. These bubbles also help evenly distribute the dissolved nutrients in the solution. Air stones do not generate oxygen on their own. They need to be attached to an external air pump via opaque food grade plastic tubing (the opacity will prevent algae growth from setting in). Air stones and air pumps are popular aquarium components and can be purchased easily at pet stores.
Net pots
Net pots are mesh planters that hold hydroponic plants. The latticed material allows roots to grow out of the sides and bottom of the pot, giving greater exposure to oxygen and nutrients. Net pots also provide superior drainage compared to traditional clay or plastic pots.
What are the 3 types of hydroponic systems?
There are hundreds of hydroponic methods, but all of them are a modification or combination of Three basic hydroponic systems.
1. Deep water culture systems
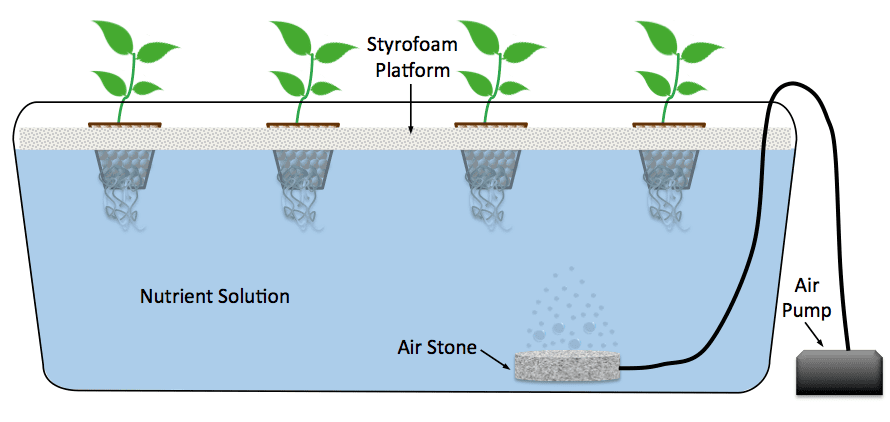
Deep water culture hydroponics are simply plants suspended in aerated water. Deep water culture systems, also known as a DWC system, are one of the easiest and most popular methods of hydroponics on the market. A DWC system dangles net pots holding plants over a deep reservoir of oxygen-rich nutrient solution. The plant’s roots are submerged in the solution, providing it with perpetual access to nutrition, water, and oxygen. Deep water culture is considered by some to be the purest form of hydroponics.
Since the root system is suspended in water at all times, proper water oxygenation is vital to the plant’s survival. If there is not enough oxygen supplied to the plant’s roots, the plant will drown in the solution. Add an air stone connected to an air pump at the bottom of the reservoir to supply oxygenation to the entire system. The bubbles from the air stone will also help circulate the nutrient solution.
It is very easy to assemble a deep water culture system at home or in a classroom without needing expensive hydroponics equipment. You can use a clean bucket or old aquarium to hold the solution and place a floating surface like styrofoam on top to house the net pots. Plants in DWC systems should only have their roots submerged in the solution. No part of the stem or vegetation should be underwater. You can even leave about an inch and a half of the roots above the waterline. The air stone bubbles will pop out of the surface and splash onto the exposed roots, so they will not be at risk of drying out
What are the advantages of deep water culture systems?
- Low maintenance: Once a DWC system is set up, there’s very little maintenance required. Just replenish the nutrient solution when needed and make sure your pump is running oxygen to the air stone. The nutrient solution typically only needs replenishing every 2-3 weeks, but this does depend on the size of your plants.
- DIY appeal: Unlike many hydroponic systems, deep water culture systems can be made cheaply and easily at home, with a quick run to your pet store and local nursery to pick up the air pump and nutrients.
2) Nutrient film technique systems
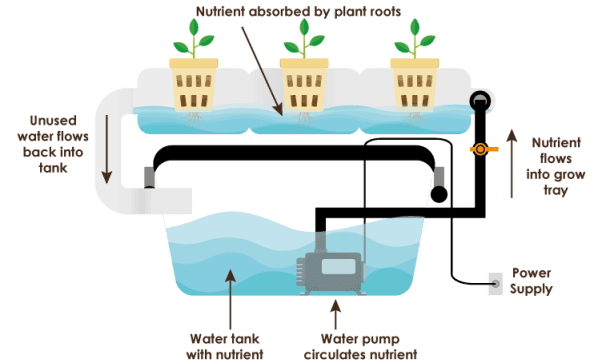
Nutrient film technique (NFT) systems suspend plants above a stream of continuously flowing nutrient solution that washes over the ends of the plant’s root systems. The channels holding the plants are tilted, allowing water to run down the length of the grow tray before draining into the reservoir below. The water in the reservoir is then aerated via air stone. A submersible pump then pumps the nutrient-rich water out of the reservoir and back to the top of the channel. The nutrient film technique is a recirculating hydroponic system. Unlike with deep water culture hydroponics, the roots of the plants in an NFT system are not immersed in water. Instead, the stream (or “film”) only flows over the ends of their roots. The roots’ tips will wick the moisture up into the plant, while the exposed root system is given plenty of access to oxygen. The bottoms of the channels are grooved, so the shallow film can pass over the root tips with ease. This also prevents water from pooling or damming up against the root systems. Even though nutrient film technique systems are constantly recycling water, it is wise to drain the reservoir and replenish the nutrient solution every week or so. This ensures your plants are being delivered ample nutrition. NFT channels must be angled at a gradual slope. If it’s too steep, the water will rush down the channel without properly nourishing the plants. If too much water is being pumped through the channel, the system will overflow and the plants can drown. NFT hydroponics are popular commercial systems, as they can support several plants per channel and can easily be mass-produced. Nutrient film technique systems are best suited for lightweight plants, like mustard greens, kale, lettuce, spinach as well as fruits like strawberries. Heavier fruiting plants like tomatoes and cucumbers will require trellises to support the excess weight.
What are the advantages of a nutrient film technique system?
- Low consumption:Since NFT hydroponics recirculate the water they do not demand large quantities of water or nutrients to function. The constant flow also makes it harder for salts to accumulate on the plant’s roots. Nutrient film technique systems also don’t require growing media, so you are saved the expense of purchasing media and the hassle of replacing it.
Modular design: Nutrient film technique systems are perfect for large-scale and commercial endeavours. Once you have one channel set up and functioning, it is very easy to expand. You can fill your greenhouse with multiple channels supporting different crops. It’s a good idea to feed each channel with a separate reservoir.

DBT Dutch Bucket System
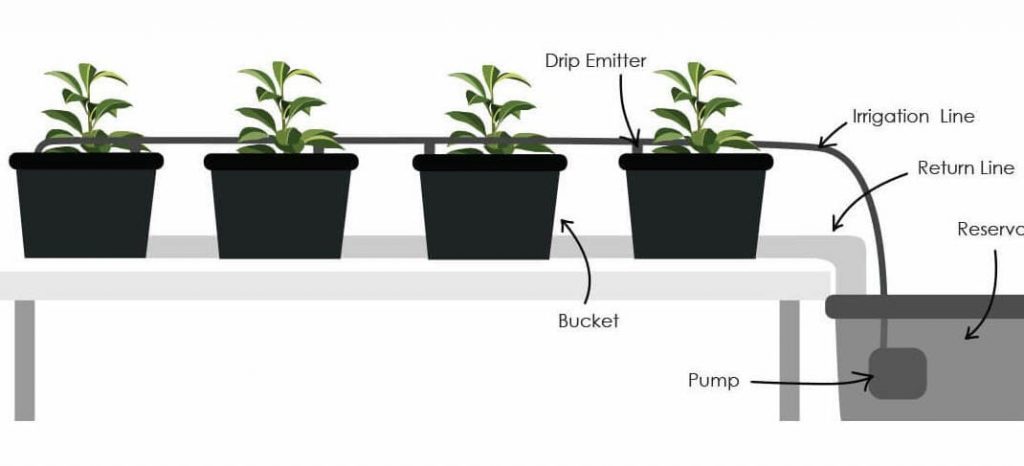
Introduction – Hydroponic Dutch bucket systems are perhaps the simplest hydroponic system to build. Each bucket can be set up separately, allowing growers to space out larger crops (like tomatoes or eggplants) without wasting media.Separate buckets can be useful in pest management as well since an infected bucket can be removed from the system without having to sacrifice an entire bed. With many types of hydroponic system, it can be difficult to grow large plants that are not the case with the dutch bucket hydr
oponic system its versatility and simplicity make it a great system for hobby hydroponic growers to efficiently a grow a lot of produce in a small amount of Space Dutch buckets are one of the popular ways to grow big plants using hydroponics. They are affordable, versatile, and reusable and are easily connected together; making a Dutch Bucket system endlessly expandable. They can be used with a large variety of different growing mediums, whether filling the whole bucket with hydroton clay pebbles or using lids with 4 inches net pots.
Advantages of Dutch bucket hydroponics
- The Dutch bucket system is great for fruiting plants, bushy, and vining plants like peppers, tomatoes, cucumbers. This system is space-saving, especially for high vining and large crops.
- Flexible in size and setup – Can scale to any size growers want convenient for pest management in case it occurs in one bucket as each bucket can be replaced easily without affecting the whole system.
- Recirculation system – All the drained water and nutrients are not lost but return to the reservoir if you set up the Dutch bucket system with the return line.
- This is a great hydroponic technique for beginners. It is easy to set up. Dutch Bucket allows starters to grow harder plants such as tomatoes, peppers and enjoy great results.
- It is well-managed systems that can conserve water and large amounts of nutrients, even in a flow-to-waste setup system.
- This system works efficiently in controlled environments for year-round growing. They help save space compared to conventional methods, mainly for vining and large crops. The majority of set-ups reduce labor for a lot of plants.
Reverse osmosis and hydroponics
- The invigorating powers of water are at the very core of hydroponics. Water bathes your hydroponic garden in nutrients, Vitalizing them and promoting their vibrant growth. If you are truly invested in the health of your plants, you should equally care about the purity of the water sustaining them. Unfortunately, most water is full of contaminants. Municipal water suppliers disinfect water reservoirs with chlorine. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, 85% of the water in the United States is hard water (meaning it contains elevated levels of calcium and magnesium). Industrial spills, agricultural runoff, and waste in landfills can leach chemicals and VOCs into the groundwater supplyReverse osmosis, (also called RO), eliminates 98% of all impurities from water by forcing it through a semipermeable membrane. Reverse osmosis strips water of heavy metals, salts, bacteria, and total dissolved solids (TDS). The result is water of remarkable purity. Using RO water for hydroponics ensures that your plants are drinking up only the nutrients you want them too. The vast majority of commercial hydroponic operations use RO water to sustain their crops. Much like hydroponics proves there is a superior way to grow plants, reverse osmosis has proven there is a superior way to facilitate this growth.
Why should I use RO water for hydroponics?
- Reverse osmosis water allows you to start with a blank slate and add precise levels of nutrients, promoters, and pH adjusters to your water. From this neutral base you can construct the ideal nutrient solution. For example, if you live in an area with hard water, your water will already contain high levels of calcium. Many hydroponic nutrient blends contain calcium, as it does encourage plant growth. However, adding a calcium-rich solution to hard water will result in nutrient imbalance. It is also much harder to measure nutrient levels in water with high levels of TDS. Most manufacturer’s instructions for nutrient solutions are based on RO water. So, if you are trying to bring the water to 800ppm of nutrients, and the water already exists at 200ppm of TDS, you will have to approximate. The results will inevitably be inaccurate. Reverse osmosis water is also lower in pH. Plants prefer acidic water, and using RO water to hydrate your crops will lessen the amount of pH regulation incumbent on you as a grower.Controlling the nutrient balance and pH level of your water is an integral component to your hydroponics’ success. If your plants are not receiving proper nutrition, it doesn’t matter how well your hydroponics system is running. A reverse osmosis system ensures that your plants are only absorbing proper nutrients dissolved in water of the highest purity.
IOT System
Features of IOT Hydroponics System
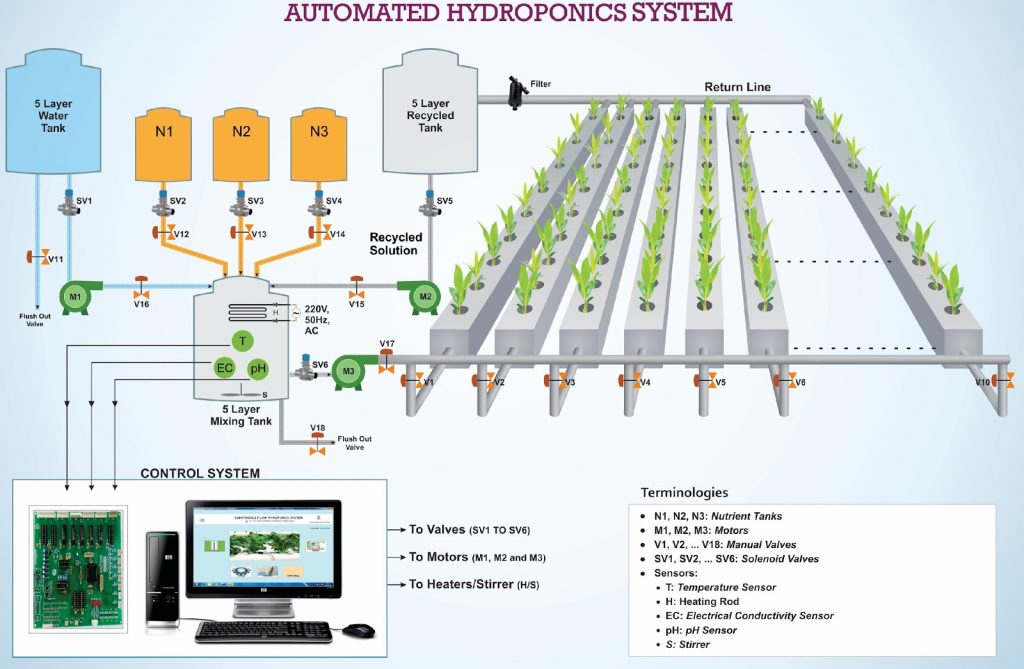
- Indigenously developed low cost automated hydroponics system
- Continuous monitoring of solution temperature, pH and conductivity
- SMS Alerts/Query, Alarm, report generation and data logging with graphical representation
- User friendly touch screen based Graphical User Interface
- GUI based Programmable control parameters
- Crop based Management System
- Use of five layered tanks for mixing and water
- Remote monitoring using SMS
Greenhouses are framed structures covered with transparent or translucent material large enough to grow crops under partial or fully controlled environmental conditions to get optimum growth and productivity. There are several types of Greenhouses i.e. Naturally Ventilated Greenhouse, Forced Ventilated Greenhouse, Shade net House etc.
Maintenance Tips
Install a trunk guard at the base of the tree to keep works its seds nutrient and water system from being cut. Trunk ours guards also …
Install a trunk guard at the base of the tree to keep works its seds nutrient and water system from being cut. Trunk ours guards also…
Install a trunk guard at the base of the tree to keep its nutrient andwater system from being cut. Trunk guards also protect trees from rodents and other small animals.
Customer Feedback
Talented Agronomist
Team Alexa made my Poly-House very well & also helped by assisting in organic Framing. Thanks & All the Best for the future.
Ms. Poonam Saxena, Indore (M.P.)
landownerExcellent job, excellent workmanship
Currently, Team Alexa helping me on Orchid Cultivation in Poly house. I’ve have to say till now everything is good and expecting the same for future.
Mr. Rajendra singh , Indore (M.P.)
landownerGreat ! Work
I would suggest Alexa Farms for Poly house Farming , Hi Tech Farming Organic Farming because there professionals have knowledge for all the crops.
Mahant Dharmendra Puri, Indore
landownerDone Wonderful job
Amazing design and installation of our new, beautiful yard. Gardener is professional, creative and knowledgeable designer.
Mark Angelino
NewyorkPlanting & Removal Charges
Within a your budget you can freshen up your plant with a few key upgrades that will increase your home’s curb appeal. A new gravel driveway or concrete walkway can make your home look like new. Small budgets are good for breaking up a larger project into manageable chunks, so you might splurge for a nice walkway this year and deal with the driveway later.













